You can turn a cube into a dynamic cube by setting a Data Binding Type property for the cube. In these configurations, data integration is based on the workspace assembly file definition and is limited to the Forms origin to meet any manual data entry requirements.
Dynamic cubes can be configured with out-of-the-box properties that support the design of specialty cubes in a similar manner as hybrid scenarios. Workspace assembly configurations are used for more advanced solutions, such as surfacing external sources in a cube.
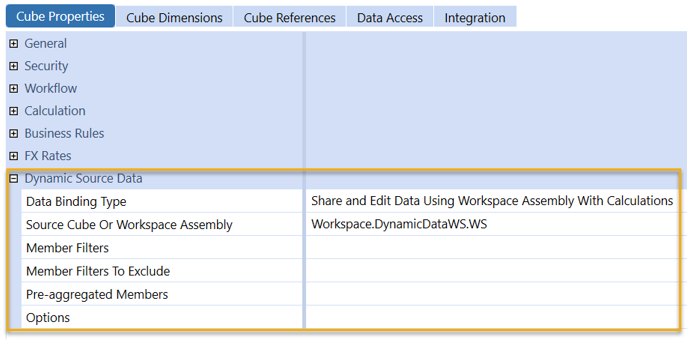
Data storage varies by use and design of the dynamic cube, as well as by the Data Binding Type property. Consider the following:
-
Copy input data options store data records in data record tables at base level intersections.
-
Share options for dynamic cubes manage the data as a pointer to the source system.
-
Dynamic cube data integration is restricted to the Forms origin member for data entry.
-
Dynamic cube data entry requires base-level intersections. O#BeforeAdj is not supported as a data entry point.
-
Dynamic cubes support write-back data to external sources and can write back text-based data through V#Annotations to external sources.
Shared data acts as a pointer to parent and base level data unit members. However, account, flow, and user-defined parent members are calculated on the fly. Base-level data unit members are required when data is integrated with a copy operation.
Data bindings have the following variations for edit and calculations:
-
Edit: Lets the dynamic cube use a workspace assembly file to write-back to the defined source, such as an external table. Note that writeback to stored cubes is not supported.
-
With Calculations: Lets dynamic cubes use workspace assembly files to execute member formulas that are stored in tables. Data is retrieved from the original source for the data unit and combined with any manual entry. Member formula calculations are stored and retrieved from regular tables, which are then merged into the results viewed in the dynamic cube.
-
CalcStatus: Is supported and defined using a workspace assembly file.
Capabilities
Dynamic Cubes support the following functions:
-
Can be used in consolidation, financial intelligence, and data unit calculation sequence adherence.
-
Data unit dimensions can be targeted for shared data.
-
Extensibility is supported.
Limitations
Consider these limitations when using Dynamic Cubes:
-
Data unit size and capacity recommendations are the same as a standard cube. Follow the best practices for Cube design.
-
Text-based data integration is restricted to V#Annotations.


