-
Start the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
The existing XFGatewayConfiguration.xml opens by default.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections to set up the Data Sources to local databases, APIs, or other on-premises resources.
More next to Local Gateway Connections to set up the Data Sources to local databases, APIs, or other on-premises resources.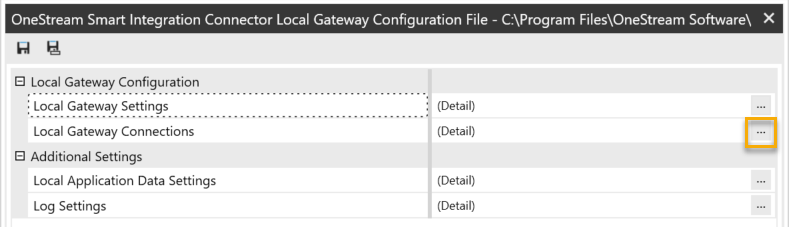
-
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source.
-
If you have a password for the connection string, enter it in the Connection String Password field. The password is masked for security. Then, when you need to enter your connection string password, use the substitution variable:
|password|
Example:Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=Sales_DB;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=|password|; -
Enter the Data Source Name, Connection String, and select a Database Provider.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
You can add as many data sources as necessary. The Data Source Name must be unique for each connection defined within a specific OneStream Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server. Names can be re-used across deployed instances of the Windows Service across your network. See below for connection string examples to a variety of relational data sources such as PostgreSQL, SQL, and ODBC, and Oracle. Connection Strings are encrypted automatically. You can edit the plain text string by clicking the ellipsis.
NOTE: Oracle databases require drivers and specific configuration provided by Oracle.
-
Click OK to save your configuration.
IMPORTANT: The connection strings below include user IDs and the password substitution variable. You can also use integrated security to remove plain text user IDs and passwords from connection strings in Smart Integration Connector. See Remove UserID and Passwords by Integrated Security.
Microsoft SQL Server
Below is an example for setting up a SQL database using the SqlClient provider.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
Data Source Name: Northeast_Sales
-
Connection String:
with UserID / Password:
Server=localhost;Initial Catalog=Sales_DB;User ID=sa;Password=|password|;Max Pool Size=1000;Connect Timeout=60; -
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select SqlClient Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
MySQL Data Provider
Below is an example for setting up a MySQL Data Provider.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source. -
Data Source Name: Sales_UK
-
Connection String:
Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=|password|;database=gatewaymysql; -
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select MySQL Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
Oracle Database Examples
Connecting to Oracle requires the download and configuration of the Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC) obtained directly from Oracle’s website. Follow the steps below to get access to these drivers and files.
-
Go to the latest web page for Oracle .NET and Visual Studio ODAC Downloads for Oracle Database.
-
After installation, the ODP.NET Provider will display as an available Database Provider in the utility when adding a new data source.
-
The connection string for Oracle databases can be set up to either reference or require a locally defined tnsnames.ora file for the requested data sources.
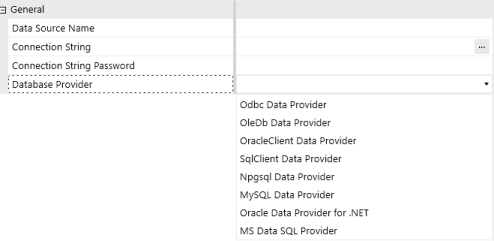
Example Connection Strings:
-
Oracle Data Provider for .NET: Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=|password|;
-
Oracle Data Provider without TNSNames.ora: Data Source=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=MyHost)(PORT=MyPort)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVER=DEDICATED)(SERVICE_NAME=MyOracleSID))); User Id=myUsername;Password=|password|;
OracleClient Database Provider
Below is an example for setting up a OracleClient database provider.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
Data Source Name: Sales_EMEA
-
Connection String: Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=|password|
-
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select OracleClient Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
Oracle Data Provider for .NET
Below is an example for setting up a Oracle Data Provider for .NET.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Data Source Name: Sales_SouthAmerica
-
Connection String:
Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=|password| -
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select Oracle Data Provider for .NET.
-
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source. -
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
PostgreSQL (Npgsql Data Provider)
Below is an example for setting up a PostGres database.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
Data Source Name: RevenueMgmtPostGres
-
Connection String: Server=localhost;Port=5432;Database=revmgt;User Id=onestream;Password=|password|;
-
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select Npgsql Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
OleDb Data Provider
Below is an example for setting up an Oracle database. This does not require additional download and configurations.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
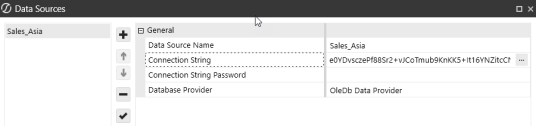
Data Source Name: Sales_Asia
-
Connection String: Provider=OraOLEDB.Oracle;Data Source=localhost:1521/XE;Initial Catalog=myDataBase;User Id=myUsername;Password=|password|;
-
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider, select OleDb Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
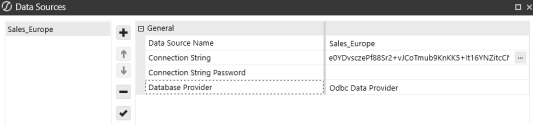
ODBC Data Provider
ODBC data sources can be defined (using a system DSN) to remove credentials from the configuration file. For ODBC connections, most ODBC drivers will allow you to set up a system DSN entry on the server, then the connection string in the gateway will be to only point to the DSN entry. See Administer ODBC data sources for more information. Below is an example for setting up an ODBC data source for Oracle.
-
Click
 More next to Local Gateway Connections.
More next to Local Gateway Connections. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. - Data Source Name: Sales_Europe
-
Connection String: Driver={Microsoft ODBC for Oracle};Server=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=199.199.199.199)(PORT=1523))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=dbName)));Uid=myUsername;Pwd=|password|;
-
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
From Database Provider , select Odbc Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to create the new source.
-
Click Save.
(Optional) Remove UserID and Passwords by Integrated Security
You can remove UserIDs and Passwords from connection strings in Smart Integration Connector if your organization has concerns over credential storage in the Smart Integration Connector Gateway configuration file. This requires running the Windows Service under a Service Account identity and using integrated security to connect to remote data sources, which eliminates local storage of any plain text credentials. Additionally, ODBC data sources can be defined (using a system DSN) to remove credentials from the configuration file.
Update the Local Gateway Connection String
-
Open your OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Open a Local Gateway Connection.
-
Navigate to the Connection String and use an Integrated or Trusted Security string. For example: Data Source=localhost,Initial Catalog=OneStream_GolfStreamDemo_2022;Trusted_Connection=True;
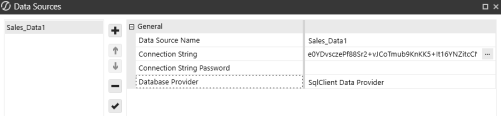
NOTE: Trusted Connections use the UserID and password you use to log into the Windows Server.
NOTE: The example above is for SQL server. Trusted connections vary by Data Provider type.
-
Click OK.
-
Save your Data Source.
Update Permissions on the OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway Service
Next, you need to update the service to run as the user. If the service is not updated, the connection does not update and errors will occur.

-
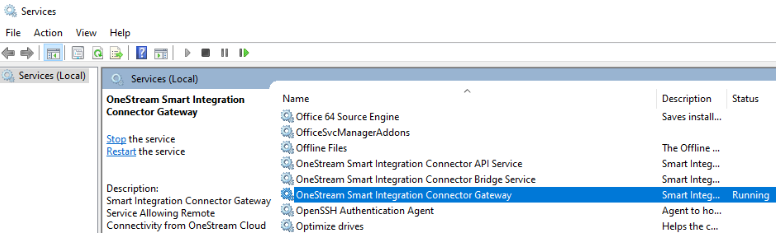
Open Windows Services.
-
Navigate to OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway. The service should be running.
-
Right-click and open Properties.
-
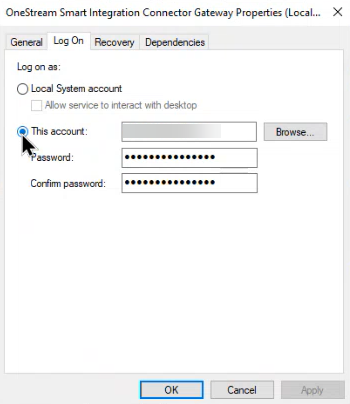
Click the Log On tab. Typically, this will default to the Local System account.
IMPORTANT: Before moving to the next step, ensure that you have the appropriate permissions and approvals from your IT Administrators to complete the Log On change. The service account used will require local Administrative rights to access resources on the Windows server, such as the machine certificate store and private keys used for encryption. This account will also require the appropriate permissions to access the database such as Microsoft SQL Server.
-
Change log on from Local System account to This account and enter your domain or login that has access to the data source. Depending on how your SSO is configured, your account could require your domain name, UserID, and password. Contact your IT Administrator if you have questions about your account domain.
-
Click Apply.
-
Click OK.
-
Right-click and select Restart to restart and update the service.
Test the Updated Integrated Connection String
You should test your connection through a Data Adapter query to verify your access to Smart Integration Connector. An alternate SQL Query to pulling the first 10-50 rows is sufficient. See Data Adapters Example.
Microsoft Entra Authentication for Azure SQL
The ability to use Microsoft Entra using service principal authentication to access Azure SQL is supported.
-
Open your OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Open a Local Gateway Connection.
-
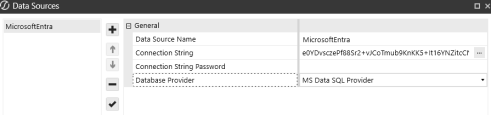
Enter a Data Source Name of MicrosoftEntra.
-
Navigate to the Connection String and enter a connection string. Example: Server=demo.database.windows.net; Authentication=Active Directory Service Principal; Encrypt=True; Database=testdb; User Id=AppId; Password=|password|;
-
Enter your Connection String Password.
NOTE: For security purposes, we recommend using the Connection String Password field and the substitution variable to ensure the password is not shown on screen. However, you can also embed the password directly within your connection string. For example: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=my_password;database=gatewaymysql;.
-
Select MS Data SQL Provider as your Database Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK.
-
Click Save.


